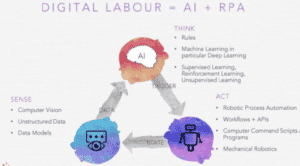
It is no secret that automation is one of the keys to a successful enterprise. Not only does it improve employees’ efficiency and productivity, but it also fundamentally improves the quality of those outcomes.
Historically, we have seen the rise of automation tools ranging from Windows-based automation to Web-based automation, to Citrix based and so on. Though effective in their own right, these tools all had something missing. Firstly, these examples lacked the ability to automate an end-to-end process involving process steps that work through heterogeneous systems, applications and technologies. Secondly, they also fell short in the “intelligence” aspect of automation. In this article we will see how Robotic and Intelligent Process Automation (RPA and IPA) fill in these gaps, as well as some example use cases and industry trends.
End-to-End Process Automation
In recent years we have seen the introduction of a number of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) tools and products. RPA is a computer software that enables anyone to configure a software robot to copy human interactions within digital systems (such as a computer) in order to execute business processes and activities. The robot has the ability to interpret, work through heterogeneous systems and applications, trigger responses, and communicate with other computer systems to perform various repetitive tasks.
RPA tools help to automate activities and tasks, irrespective of whether the applications are running on the web, on the desktop/windows, or in a virtual environment. They also provide automation around applications such as Excel, PDF, Email, Database, APIs, and many more. (RPA can also be a useful tool in integration – check out another blog here).
RPA tools are still evolving, and are constantly accumulating exciting new capabilities around ‘Intelligence’. For example there are RPA tools which can see the screen (computer vision), listen (natural language processing), write (natural language generation), comprehend/understand the text and unstructured data, extract text from images, identify objects in images, and perform machine learning and other cognitive capabilities. The automation of business processes that leverage these artificial intelligence and cognitive technologies alongside RPA is called Intelligent Process Automation (IPA).
Example Use Case
Imagine the job of a recruitment consultant working on the contractors “onboarding” process with the following process steps:
- High level onboarding process steps
- Check any onboarding request in System 1 (Windows application)
- Request contractor to provide details such as bank account details etc and sign the documents using Email
- Check work rights, perform police checks in System 2 (Web application)
- Request timesheet and payroll access in System 3 (Legacy System)
- Prepare and send a contract in System 4 and using email
Using RPA
With only RPA the above steps in the “onboarding process” can be (partially or fully) performed by a bot depending on the human intervention required, complexity, etc. The RPA tools can replace manual clicks and trigger a process when emails are received, create folders, download the email attachments, and login to System 1, System 2, System 3 and System 4 to perform various tasks as part of the “onboarding” process automation. There are hundreds of activity/task packages that come with RPA tools: these include upload or download files to/from the remote server, query against the databases, work with the excel file – read/write operations, read the word document and PDF files, calling APIs, and many more.
Using RPA with Intelligence
In addition to RPA automating the above process steps, “Intelligent” bots can read and comprehend emails, and prepare a non-templated response. The bot can understand and score the mood of the email sender and potentially categorise them into urgent vs non-urgent based on the content of the email, and can continuously improve with time using machine learning. The “intelligent” bots are underpinned by technologies such as OCR (Optical Character Recognition) to extract text from images, NLP (Natural Language Processing) to accept voice commands, and NLG (Natural Language Generation) to convert technical analytical stats into human, readable, grammatically correct, plain-English sentences that a non-technical person could easily understand.
RPA and IPA stats
Businesses are finding these tools appealing because they’re non-intrusive and leverage existing infrastructure without causing disruption or requiring underlying systems to be replaced. Essentially, efficiency and compliance are no longer an operating cost, but instead a by-product of these tools.
According to a 2018 study by Deloitte 72% of enterprises intend to implement RPA/IPA within the next two years. The same study found that the enterprises that had implemented process automation had tangible benefits within less than 12 months; an average of 20% of full-time equivalent capacity provided by robots, 92% improved compliance, 90% improved quality/accuracy, 86% improved productivity and 59% cost reduction.
RPA Use Cases
- Credit assessment
- Fraud detection
- Streamlining operations across department
- Delivering insights
- Screen scraping
- Automating excel without having it installed
- Automating without code
- Streamlining and automating across systems
- Data migration
- CRM updates
- Software installations
- Hiring and onboarding
By 2021, Forrester estimates that there will be more than 4 million robots doing office and administrative work as well as sales and related tasks.
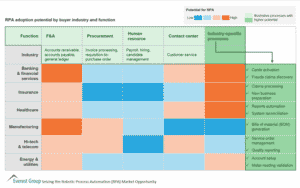
Functions within different industries and the potential for RPA to complete those functions – blue represents low potential and orange high potential.
IPA Use Cases
- Cross sell in banking
- Churn prediction
- Automating Common Customer Requests
- Demand predictions from logistics
- Price optimisation
- Data maintenance
- Auditing
- Social media marketing
In summary, Robotic Process Automation with Intelligence is better than RPA alone because it can process unstructured data, handle exceptions, and continuously learn. The evolution of RPA to IPA and the penetration of these tools and technologies in the industry is inevitable.
So, are you ready for the “Intelligent” bots?